Denis Yardin, one of our incredibly talented and passionate Osteopaths, clarifies the mystery and misunderstanding behind his profession and explains the many benefits behind Osteopathy.
Osteopathy has exploded in popularity in Australia. Many people have started to visit them for their aches and pains without having a clear understanding of who they are and what they do. It is therefore our responsibility as health care providers to give an insight into how Osteopaths can help people within the community.
So, what is Osteopathy and why do people choose to see one? This blog aims to create an informative view on the profession of Osteopathy and how it can benefit people, along with examples to illustrate when someone would benefit from seeing an Osteopath.
WHAT IS OSTEOPATHY?
The International Academy of Osteopathy defines osteopathy as “a manual examination and treatment method of the integrated musculoskeletal, visceral system and craniosacral systems.”
Osteopaths assess the mobility and flexibility of the musculoskeletal, the vascular, the neurological, the visceral and fascial systems in all its integration. They value how the structure and function of those systems are interrelated and how the body uses its own self-healing mechanism to recover from injuries.
Examples of how an Osteopath would treat a patient could be as follows…
1. Hip Problem
A hip problem for instance may be resulting from multiple causes such as mechanical problems in the foot or knee, movement blockages within the pelvic joint, low back issues, or even circulation problems that may be related to the internal organs such as constipation.
An overall assessment of movement and specific musculoskeletal testing of several body structures are then used to differentiate between the tissues being affected and what are causing the problem. Once the origin of the condition is identified, the Osteopath uses a variety of manual techniques and exercise prescriptions, as well as patient education to help with the expected tissue healing prognosis.
2. Kidney problem
The visceral system includes all the organs present in the chest and abdominal cavity. A kidney problem may affect the mobility of the visceral fascia (connective tissue that connects/links the organs and all other tissues together within the body) which can lead to mobility/flexibility limitations in the musculoskeletal system, particularly around the torso where segmental neuronal supply is shared between the kidneys and skin/muscles.
An aspect of neural input to these organs relate to specific spinal cord segments. Therefore, a pain signal originating from an internal organ may affect muscles and skin that share the same spinal cord segment, and as a result, a patient may experience musculoskeletal pain without having any injury.
Specific visceral manipulation techniques may be used to encourage space within the abdomen to allow tension through fascia to free itself. Gentle manipulation technique is utilised with patient’s breathing which may relieve some discomfort. The Osteopaths may then reassess the patient’s back pain and treat where necessary.
Why should you choose to see an Osteopath?
Osteopaths conduct a comprehensive assessment to identify mobility impairments within the body systems and investigate the exact cause of the problem. We mainly use hands-on assessments and treatment techniques to manage structural and bio-mechanical dysfunctions with a holistic approach to assist with health optimisation. Those manual techniques are relatively gentle and are usually aimed at structures such as muscles, ligaments, tendons, joints, fascia and other connective tissues.
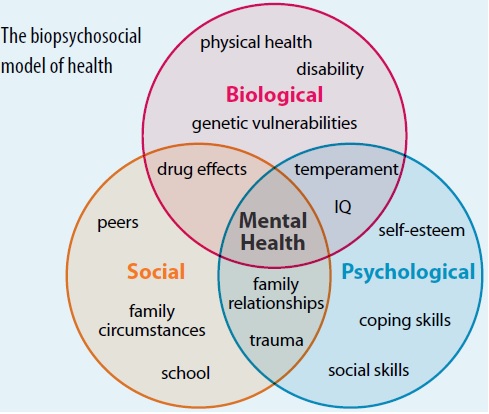
The biopsychosocial model of health is frequently mentioned by Osteopaths as it is aligned with our treatment approach. It is the belief that biological, psychological and social factors play a profound role on how pain is perceived and dealt with by patients. Those factors are interrelated and display a complex relationship within themselves as shown in the diagram below.
An illustration of the biopsychosocial model comprised of biological, psychological, and sociological influences.
Source: researchgate.net
A patient-centered approach is taken, which considers the person in their entirety, including their goals, needs and expectations. Osteopathy is all about holism and therefore may also collaborate with other allied health modalities, to best consider patient outcomes.
Osteopaths educate patients regarding their condition and the different management strategies based on the latest evidence. They would hence always explain why they choose to do a manual therapy technique and what they aim to achieve during their consultation.
Who may benefit from seeing an Osteopath in the community?
Osteopaths are trained to assess and treat people of all demography with various presentations. Many people are unaware that the service can be provided in the community. Some short scenarios examples have therefore been prepared to give some ideas of what conditions may benefit from seeing an Osteopath.
Recurrent injury of unknown cause
A patient has tennis elbow or a suspicion of tennis elbow. However, he has never played tennis or had no recent trauma. The injury keeps on coming back despite taking medications or making some lifestyle changes.
Pain with no known underlying pathology
Pain is suddenly felt over the right knee. The pain is now present every day and impacts the patient’s ability to perform daily tasks. An X-ray has been performed and revealed no internal damage or pathology.
Mobility impairment that is generally non-traumatic
A patient is having a gradual decline in mobility. There have been no trauma or surgery to the legs. They have a known circulation problem and they feel weak.
A complex case where many allied health avenues were tried and had no significant change or result
A patient has been suffering from chest pain for more than 10 years. They have a long list of medical history. The patient has seen GPs, specialists, physiotherapist, psychologist to name a few. Medication administration lead to various side effects and therefore chose to stop them.
Patients that are seeking more passive treatment
A patient is very sensitive to touch and any manual treatment technique used in the past caused great pain. They also want to be involved in a treatment that would help in relaxation.
Chronic pain patients with multiple comorbidities
A patient with multiple conditions also …